อุบัติเหตุที่ได้รับบริเวณใบหน้า โดยเฉพาะได้รับอุบัติเหตุบริเวณดวงตาหรือเบ้าตา มีความจำเป็นต้องได้รับการตรวจวินิจฉัยโดยจักษุแพทย์ อย่างละเอียดเพื่อประเมินความรุนแรง อุบัติเหตุที่เกิดบริเวณใบหน้าได้แก่ เปลือกตา การมองเห็น ดวงตา ท่อน้ำตา เบ้าตา และกระดูกใบหน้า จักษุแพทย์เฉพาะทางด้านเปลือกตา ท่อน้ำตา และเบ้าตา หรือที่เรียกว่า Oculoplastic Specialist (Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery) จึงมีความเชี่ยวชาญเฉพาะโรคดังกล่าวเป็นพิเศษ และสามารถให้การประเมิน วินิจฉัยภาวะเหล่านี้และแนะนำวิธีรักษาได้อย่างถูกต้องและครบถ้วน สามารถอธิบายข้อดีข้อเสียของการเข้ารับการรักษาได้อย่างถูกต้อง
ภาวะกระดูกเบ้าตาแตก หรือที่เรียกว่า Orbital Blow-out Fracture
เรียบเรียงโดย นพ. ณัฐวุฒิ วะน้ำค้าง, พ.บ.
Orbital fracture เป็นภาวะที่พบบ่อยในผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับอุบัติเหตุจากการกระแทกทีี่บริเวณใบหน้าและกระโหลกศรีษะ การบาดเจ็บอาจพบได้ในหลายอวัยวะได้แก่ ดวงตา (globe) เปลือกตา (eyelids) ระบบท่อน้ำตา (lacrimal system) กระดูกรอบๆเบ้าตาและกระดูกเบ้าตา กระดูกโพรงไซนัส (sinuses) และสมอง (brain) เพราะฉะน้ันการตรวจร่างกายทางจักษุวิทยาจึงมีความสำคัญมากที่จะบอกถึงรายละเอียดของการบาดเจ็บว่ามีทีส่วนใดบ้าง บางครั้งหลังได้รับอุบัติเหตุใหม่ๆการประเมินความบาดเจ็บอาจบอกได้ยากเพราะอวัยวะรอบๆดวงตาอาจมีลักษณะฟกช้ำและบวม (Eyelid and orbital edema) ดังนั้นถ้าผู้ป่วยได้รับอุบัติเหตุเบ้าตาเมื่อภาวะบวมช้ำของเปลือกตา เบ้าตา และใบหน้า จากการได้รับอุบัติเหตุ ลดลงแล้ว
Orbital fracture สามารถแบ่งออกได้เป็น
Internal fractures หมายถึง ภาวะ fracture ที่เกิดขึ้้นกับ orbital walls เท่านั้น
External fractures หมายถึง ภาวะ fracture ที่เกิดขึ้้นกับ orbital rims และ adjacent bones
Complex fractures หมายถึง ภาวะ fracture ที่เกิดขึ้้นทั้ง orbital walls และ orbital rims
Blow-out fractures หมายถึง ภาวะ internal fracture ที่เกิดขึ้้น เฉพาะ orbital wall และไม่รวมถึง orbital rim ภาวะ fracture นี้จะเป็นผลให้ชิ้นส่วน ของกระดูกที่แตก ( bone fragments ) เคล่ือนที่ออกไปอยู่ในต่ำแหน่งของกระดูก sinus ข้างเคียง
Trapdoor fractures เป็นภาวะที่ส่วนของกระดูก orbital flooor ที่แตก เคลื่อนผิดตำแหน่ง่ออกไปโดยที่ส่วนหนึ่งของชิ้นกระดูกนั้นในด้านใดด้านหนึ่งยังติดอยู่กับตำแหน่งเดิม ซึ่งทำให้เกิดลักษณะคล้ายบานพับ ซึ่งอาจเป็นผลให้เกิด muscle entrapment ได้ trapdoor fracture มักจะเกิดได้บ่อยในกลุ่มผู้ป่วยเด็กมากกว่าผู้ใหญ่
Blow-out fracture เป็นชนิดของการบาดเจ็บที่จะมาพบจักษุแพทย์มากที่สุด โดยการแตกของกระดูกมักจะเกิดเมื่อมีวัตถุมากระแทก orbital cavity แล้วเกิดแรง retropulsion ของ orbital content ทำให้เกิดแรงดันสูงขึ้นอย่างรวดเร็วภายในเบ้าตา เป็นผลให้ กระดูกเบ้าตาทางด้าน floor โดยเฉพาะด้าน medial ต่อ infraorbital groove และ medial wall ซึ่งบางมากแตกออกได้
อาการที่มักพบร่วมกับ blow-out fracture ได้แก่
Diplopia
Strabismus
Pain on extraocular movement
Enophthalmos
Infraorbital hypoesthesia
Nausea and vomiting มักพบได้ใน trapdoor fracture โดยเฉพาะในเด็ก
ผู้ป่วยควรได้รับการตรวจ complete ophthalmologic examination เพื่อตรวจหาอาการ บาดเจ็บที่อาจพบร่วมด้วยได้แก่ hyphema, retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, lens subluxation, iridodialysis, ruptured globe, traumatic optic neuropathy, orbital compartment syndrome หรือ กระดูกแตกที่บริเวณกระโหลกและใบหน้า
Ocular motility examination
โดยการตรวจ ocular alignment ใน primary และ eccentric gaze position ซึ่งถ้าพบมี limitation of ocular motility ก็แสดงว่าอาจจะมี entrapment หรือ restriction ของ extraocular muscle หรือ orbital soft tissue รอบๆ กรณีมี entrapment of inferior rectus ตรงตำแหน่งของ floor fracture มักจะทำให้เกิด limitation of supraduction (upgaze) หรือ infraduction (downgaze) กรณีมี entrapment of medial rectus มักทำให้เกิด limitation of abduction หรืิอ adduction สำหรับ Muscle paresis นั้นอาจเกิดจาก direct injury กับ ocular muscle เองหรืออาจเกิดจาก cranial nerve injury บางครั้งภาวะ Strabismus และ Diplopia ที่เกิดในช่วงแรกต่อมาจะหายไปได้เองในภายหลัง ซึ่งภาวะเหล่านี้มักเกิดจาก orbital hemorrhage หรือ orbital edema
Forced duction test
สามารถใช้แยกระหว่าง muscle restriction และ muscle paresis บางครั้งหลังได้รับ อุบัติเหตุร่วมกับมี orbital hemorrhage and edema สามารถทำให้เกิด moderately positive forced duction test ได้ ปกติมักแนะนำให้รอจนอาการบวมหายเสียก่อนจึงตรวจ test นี้ ในรายที่มี Trapdoor fracture มักตรวจพบว่ามี True muscle restriction และมักมี severe pain เมื่อ พยายามทำ supraduction กรณีผู้ป่วยเด็ก การทำ Forced duction test นั้นจะยากมาก จึงควรทำเมื่อได้ sedation เด็กแล้ว
Binocular diplopia
มักจะเกิดขึ้นเสมอถ้ามี muscle restriction มักแนะนำให้ผ่าตัดแก้ไขเมื่อมี Diplopia ภายใน central 30 degree of fixation
Enophthalmos
เมื่อเกิด blow-out fracture กระดูกเบ้าตาจะยุบตัวออกไปทางด้านนอก ทำให้มีการเพิ่มของ orbital volume ร่วมกับมี orbital tissue prolapse เข้าไปใน sinus ข้างเคียง และทำให้เกิด Enophthalmos ในช่วงแรกหลังได้รับอุบัติเหตุ อาจพบว่ามีภาวะ Exophthalmos จาก edema and hemorrhageได้ เมื่อเวลาผ่านไประยะหนึ่งแล้วอาการตาโปนจะดีขึ้นเมื่ออาการบวมยุบลง และ globe จะมาอยู่ในตำแหน่งที่ถูกต้อง ถ้าทิ้งไว้เมื่อระยะเวลาผ่านไป อาจพบว่ามี scarring และ fat atrophy ได้ ซึ่งทำให้เกิดภาวะ enophthalmos มากขึ้น การประเมินเราสามารถใช้ Hetel or Naugle exophthalmometer วัดปริมานของ globe displacement ใน axial axis ถ้าพบว่ามีการ เปลี่ยนแปลงมากกว่า 2 mm จะถือว่าผิดปกติ
Hypo-ophthalmos
เป็นลักษณะของ downward globe displacement มักเกิดในกรณที่ีมี large orbital wall fracture โดยจะตรวจพบว่ามี inferior corneal limbus อยู่ต่ำกว่า inferior lid margin การตรวจ สามารถใช้ไม้บรรทัดตรวจและบอกปริมาณของ downward or upward displacement ได้
Facial hypesthesia
inferior orbital wall ทางด้าน medial ่เป็นส่วนที่บางมากและแตกง่าย ซึ่งคลุมอยู่เหนือ infraorbital groove ถ้า fracture site ขยายไปถึงบริเวณของ infraorbital groove ซ่ึงมี infraorbital artery , vein and nerve (CN1)อยู่ ผู้ป่วยมักมี facial sensation ลดลง หรือชา บริเวณเปลือกตาล่างและโหนกแก้มส่านบน
Orbital rim fracture
สามารถตรวจได้โดยการคลำ จะตรวจพบลักษณะของ bony step offs หรืออาจพบลักษณะของ crackling sound (crepitus) ซึ่งเป็นลักษณะของ orbital emphysema โดยมักพบเกิดจาก medial wall fracture และมี air จาก paranasal sinus ออกมาอยู่ที่ orbital soft tissue ภาวะนี้มักจะหายเองและผู้ป่วยจำเป็นต้องหลีกเลี่ยงการจามซึ่งทำให้เป็นมากขึ้นได้
Radiographic Evaluation
ในรายที่สงสัยควรส่งทำ CT scan เพื่อตรวจดูภาวะ internal blow-out fracture และ craniofracture อื่นๆ ควรส่ง CT scan ดู coronal, axial and saggital view ความถี่อย่างน้อยทุก 2 mm เพื่อดู detail of orbital bone, extraocular muscle and orbital soft tissue เพราะภาวะ restricted motility จากการตรวจอาจเกิดได้ทั้งจาก entrapped muscle หรือ soft tissue
Treatment
การตรวจร่างกายและ CT scan มีบทบาทสำคัญมากในการวางแผนการรักษาเป็นอย่างมาก ในปัจจุบันมีข้อบ่งชี้ในการผ่าตัดได้แก่
symtomatic diplopia ภายใน 30 degree ของ primary gaze
พบว่ามี muscle entrapment จาก CT scan และ/หรือ ตรวจพบว่ามี positive forced duction test
มี large fracture ขนาดมากกว่า 50% ของขนาดพื้นที่ของ orbital floor ท้ังหมด
Displaced orbital rim fracture และ/ หรือ พบ associated facial fracture, มี enophthalmos มากกว่า 3 mm
พบมี hypo-ophthalmos อย่างชัดเจน
กรณีตรวจพบว่ามี muscle entrapment อย่างชัดเจนจากการตรวจร่างกายและ CT scan ผู้ป่วยควรได้รับการผ่าตัดรักษาภายใน 48 ชั่วโมง เพื่อป้องกัน ischemic damage ของ extraocular muscle และ tissue necrosis
บางกรณีอาจเลือกรักษาตามอาการและติดตามอาการไปก่อนพิจารณาผ่าตัด ได้แก่
symptomatic diplopia ภายนอกช่วง 30 degree ของ primary gaze โดยที่ไม่มี muscle entrapment ชัดเจน
ขนาดของกระดูกที่แตกมีขนาดปานกลาง
มีอาการแสดงที่บ่งชี้ว่ามีอาการดีขึ้นภายในช่วง 1-2 สัปดาห์ หลังจากอาการบวม ยุบหายไปแล้ว้
การผ่าตัดรักษา orbital fracture สามารถผ่าตัดได้ 2 วิธีใหญ่ๆ คือ transcutaneous and transconjunctival approach สำหรับ transcutaneous approach นั้นสามารถมี incision site ได้แก่ infraciliary, lower lid crease และ orbital rim margin ส่วน tranconjuntival approach นั้นได้รับความนิยมมากกว่าเพราะสามารถให้ excellent exposure และ ลดโอกาศเกิด postoperative lid retraction และ ectropion ได้ดีกว่า
ในปัจจุบันมี orbital implant อยู่หลายชนิดได้แก่ autogenous และ alloplastic implant Autogenous implant นั้นประกอบด้วย bone graft, cartilage หรือ fascia ต่ำแหน่งที่นิยม harvest bone graft ได้แก่ cranium, iliac crest หรือ rib ข้อดีของ autogenous implant คือมี excellent biocompatibility ข้อเสียคืออาจเกิด partial resorption ได้ ซึ่งอาจเกิด late-onset enopthalmos ได้และยังใช้เวลานานกว่าปกติในการ harvest graft รวมถึงอาจเกิด morbidity ทีี่ donor site ได้ ส่วน Alloplastic implant นั้น ในปัจจุบันมีทั้งชนิด porous, nonporous และ absorbable ข้อดีของ porous implant คือ สามารถตัดเป็นรูปร่างตามต้องการได้ และ สามารถมี fibrovascular ingrowth ซึ่งจะช่วยเรื่อง ลดโอกาศเกิด migration และ infection ในปัจจุบัน porous implant ที่มีขายอยู่ ประกอบด้วย hydroxyapatite และ high-density porous polyethylene (Medpore) ข้อจำกัดของ hydroxyapatite คือ แข็ง, แตกง่าย และจัดรูปทรงยาก สำหรับ high-density porous polyethylene จะอยู่ในรูปแผ่นบางๆ หลายขนาดให้เลือก สามารถตัดให้เข้ารูปทรงที่เหมาะสมและ fixation ได้ง่าย สำหรับ metallic implant นั้นจะมีหลายรูบแบบ ได้แก่ micro หรือ mini plate, mesh หรือ grids วัสดุที่ใช้ทำเป็น titanium หรือ vitalium ส่วนใหญ่ จะนำมาใช้ใน orbital rim fracture หรือ large, extensive orbital floor fracture สำหรับ Absorbable implant นั้นทำมาจาก polyglactin หรือ gelatin film มักใช้ใน small fracture แต่ในปัจจุบันมี LactoSorb ซึ่งเป็น longer lasting absorbable implant
Complication ที่พบได้หลัง internal blow-out fracture repair ได้แก่ visual loss, postoperative orbital hemorrhage, persistent enophthalmos/ hypo-ophthalmos, diplopia and complication ที่เกิดจาก orbital implants ซึ่งอาจพบได้ ได้แก่ infection, inflammation, migration และ extrusion โดยสรุป complication เหล่านี้สามารถหลีกเลี่ยง ได้โดย เลือกวิธีผ่าตัด, ชนิดของ implant และ surgical techniques ที่เหมาะสม
References
Meyer DR. Orbital fractures. In: Tasman W, Jaeger EA, eds. Duane's Clinical Ophthalmology, rev. ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lipincott-Raven; 1996:Chap 48.
Bansagi ZC, Meyer DR. Internal orbital fractures in the pediatric age group: characterization and management. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:829-836..
Koltai PJ, Amjad I, Meyer DR, Feustel PJ. Orbital fractures in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995;121:1375-1379.
Dutton JJ, Manson PN, Iliff N, Putterman AM. Management of blow-out fractures of the orbital floor. Surv Ophthalmol. 1990;35:279-280.
Westfall CT, Shore JW, Nunery WR, et al. Operative complications of the transconjunctival inferior fornix approach. Ophthalmology. 1991;98:1525.
Meyer DR. Alloplastic materials for orbital surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1995;6:43.
Enislidis G, Pichorner S, Kainberger F, Ewers R. Lactosorb panel and screws for repair of large orbital floor defects. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1997;25:316-321.
Abel AD, Meyer DR. Blow-out fracture in adults and children. Ophthalmic Hyperguide, section Oculoplastics.
Koh JY, Della Rocca RC, Maher EA. Orbital fractures: Diagnosis and management. In: Albert DM. Ophthalmic surgery, Principles and Techniques, Massachusetts: Walsworth ; 1999: chap 90.
คำอธิบาย
รูปที่ 1. ผู้ป่วยเด็กอายุ 9 ปี ได้รับอุบัติเหตุทางรถยนต์ มี severe inferior and medial wall fracture พบมี significant inferior and medial displacement of right globe.
รูปที่ 2. ผู้ป่วยชายไทยอายุ 20 ปี จากการตรวจร่างกายพบมี limitation of supraduction (upgaze)
รูปที่ 3. Worm’s eye view พบมี significant enophthalmos ในตาข้างซ้าย สามารถตรวจได้ง่ายๆ โดยให้ผู้ป่วยเชยคางขึ้นและผู้ตรวจตรวจดูตำแหน่งของ globe ทั้ง 2 ข้างเปรียบเทียบกัน (เรียก Worm’s eye view เพราะเหมือนลักษณะหนอนมองขึ้น)
รูปที่ 4. รูปแสดง absorbable implant (LactoSorb) [รูปทางซ้าย] และ Titanium plate [รูปทางขวา]
รูปที่ 5. รูปภาคตัดขวางแสดง preseptal and post septal transconjunctival approach
รูปที่่ 6. รูปภาคตัดขวางแสดง transcutaneous inferior orbitotomy, skin-muscle flap subcillary approach
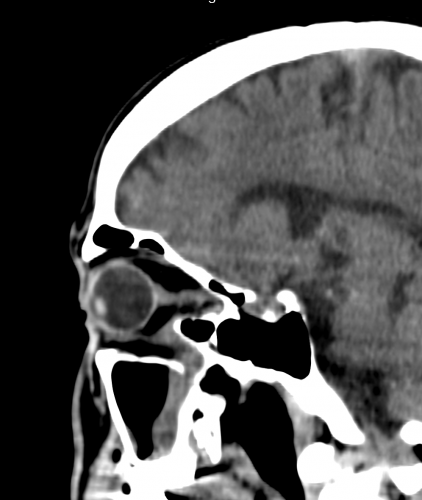
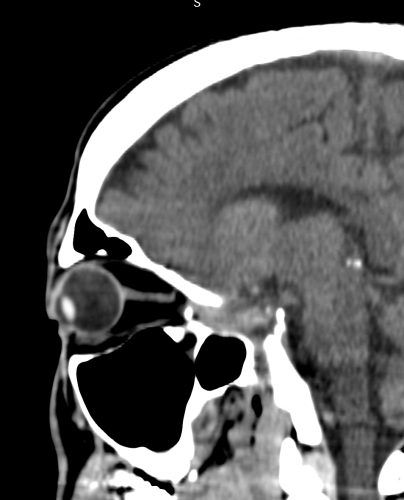
รูปที่ 7 CT orbit (coronal view): Large medial wall fracture with entrapped medial rectus
รูปที่ 8 CT orbit (saggital view): larger inferior orbital wall fracture with entrapped inferior rectus